As a refresh from our last article, our world today is composed of security incidents and data breaches that we must identify and resolve before we, ourselves, are compromised.
In today’s article, we will dive into the transformative dangers of tech, as we all know the benefits of how the lightbulb and iPhone paved way for society.
Here’s a little joke: Why did the computer go to therapy? It couldn’t decide whether it was a bug or a feature!
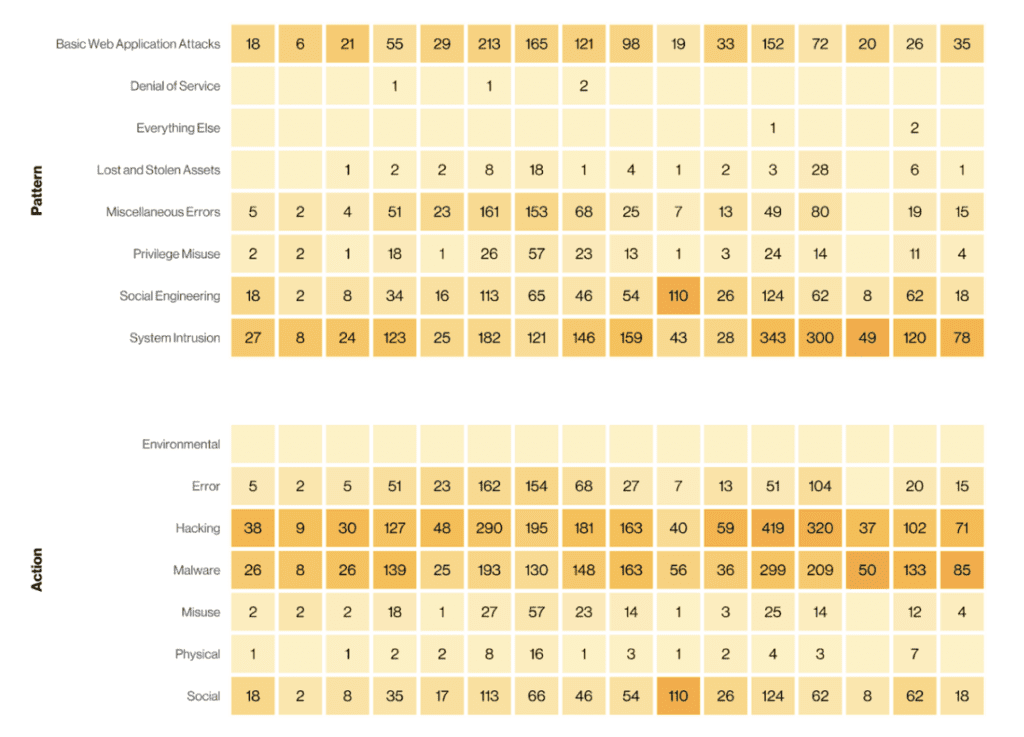
This is completely true! The issue at hand is that data is constantly being generated, shared, and stored, and the threat of security incidents and data breaches looms large. These incidents can have far-reaching consequences, impacting individuals, organizations, and even entire nations. Understanding the various action categories through which such incidents occur is crucial in comprehending the complexity of these events. These action categories include hacking, malware, errors, social engineering, misuse, physical breaches, and environmental factors. By delving into each category, we can gain insights into how security incidents unfold and the potential ramifications they can have.
Types of Actions
1. Hacking
One action category that often comes to mind when we think of security incidents is hacking. This involves unauthorized individuals gaining access to systems or networks through various means such as exploiting vulnerabilities or employing sophisticated techniques. Once inside, hackers can steal sensitive information, disrupt services, or launch further attacks. Recent examples of hacking incidents include the high-profile breaches of major corporations’ databases, resulting in the compromise of millions of user records and financial losses.
2. Malware
Another prevalent action category in security incidents is malware. Malware refers to malicious software designed to infiltrate systems and carry out harmful actions. This can include viruses, worms, ransomware, or spyware. Malware is typically spread through infected email attachments, compromised websites, or malicious downloads. Once installed, it can enable unauthorized access, data theft, or system disruption. The impact of malware can be widespread, affecting individuals, businesses, and critical infrastructure.
3. Errors
Not all security incidents are caused by malicious intent. Errors, both human and technological, can also lead to breaches. Human errors can involve inadvertently sharing sensitive information, misconfiguring systems, or falling victim to social engineering tactics. Technological errors can stem from software bugs, system misconfigurations, or faulty hardware. Despite their unintentional nature, these errors can still result in the unauthorized exposure of sensitive data or system vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malicious actors.
4. Social Engineering
Social engineering is a category that relies on manipulating individuals rather than technological vulnerabilities. In these incidents, attackers deceive or manipulate individuals into divulging sensitive information or granting unauthorized access. Social engineering tactics can include phishing emails, phone scams, or impersonation. By exploiting human psychology and trust, attackers can gain access to confidential data or compromise systems without needing to employ sophisticated technical methods.
5. Misuse
Sometimes, security incidents occur as a result of internal misuse or abuse of privileges. This can involve authorized individuals within an organization intentionally accessing or using data inappropriately. Misuse can range from accessing sensitive information without authorization to intentionally sabotaging systems or leaking data. Incidents involving misuse can be challenging to detect, as the individuals responsible often have legitimate access rights.
6. Physical Breaches and Environmental Factors
While much of the focus in cybersecurity is on digital threats, physical breaches and environmental factors can also play a role in security incidents. Physical breaches occur when unauthorized individuals gain physical access to premises or systems, bypassing physical security measures. Environmental factors, such as natural disasters or power outages, can disrupt critical infrastructure, leading to data loss or system downtime. These incidents highlight the importance of implementing robust physical security measures and disaster recovery plans.
With this in mind, we will discuss the most prominent types of security incidents and data breaches.
Types of Security Incidents
Firstly, a security incident refers to any event or activity that compromises the security of a system, network, or data. It can include unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, or human errors.
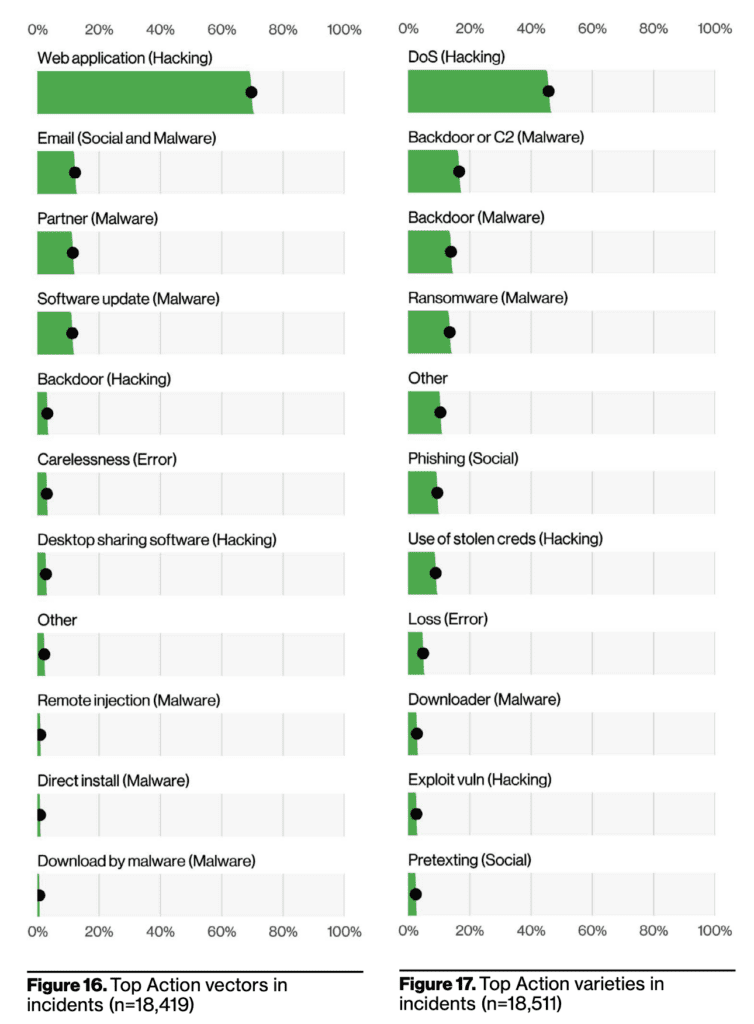
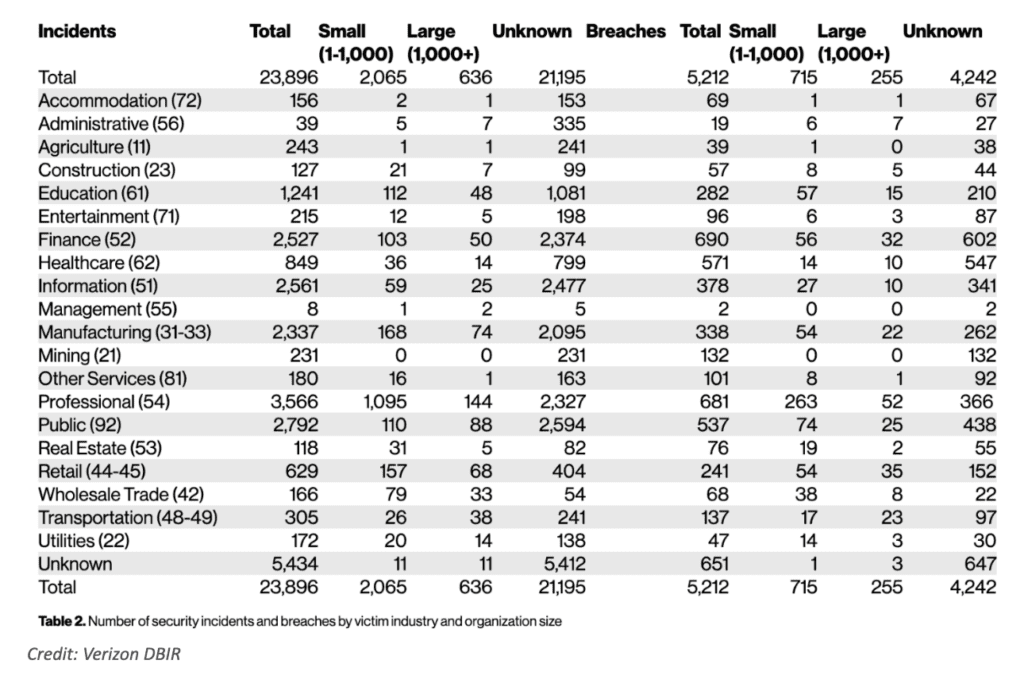
According to the above charts, we can see that web application and DoS (denial of service) hacking are the 2 most common action vectors in security incidents.
For more information about these two varieties, web application hacking and denial of service (DoS) attacks are both forms of hacking that target computer systems or networks, but they differ in their objectives and methods.
Web application hacking involves exploiting vulnerabilities in web applications to gain unauthorized access or manipulate the application’s functionality. Attackers may exploit weaknesses in the application’s code, configuration, or user inputs to carry out various malicious activities, such as stealing sensitive information, defacing the website, or taking control of the underlying server. The goal of web application hacking is typically to compromise the security and integrity of the targeted application.
On the other hand, a DoS attack aims to disrupt or disable the normal functioning of a network, system, or service by overwhelming it with a flood of malicious traffic or resource requests. In a DoS attack, the attacker floods the target with an excessive volume of traffic or exploits vulnerabilities to exhaust system resources, such as bandwidth, processing power, or memory. The objective of a DoS attack is to render the targeted system or network unavailable to its intended users, causing service disruptions or downtime.
While web application hacking and DoS attacks have distinct objectives and methods, they share some similarities. Both types of attacks involve exploiting vulnerabilities in computer systems or networks. They can cause significant damage to organizations by compromising sensitive information, disrupting services, and undermining user trust. Additionally, both web application hacking and DoS attacks require a certain level of technical expertise and knowledge of system vulnerabilities to be executed effectively.
Types of Data Breaches
Secondly, data breaches specifically involve the unauthorized access, disclosure, or loss of sensitive or confidential information. While a security incident can be any security-related event, a data breach is a specific type of incident that involves the compromise of data itself.
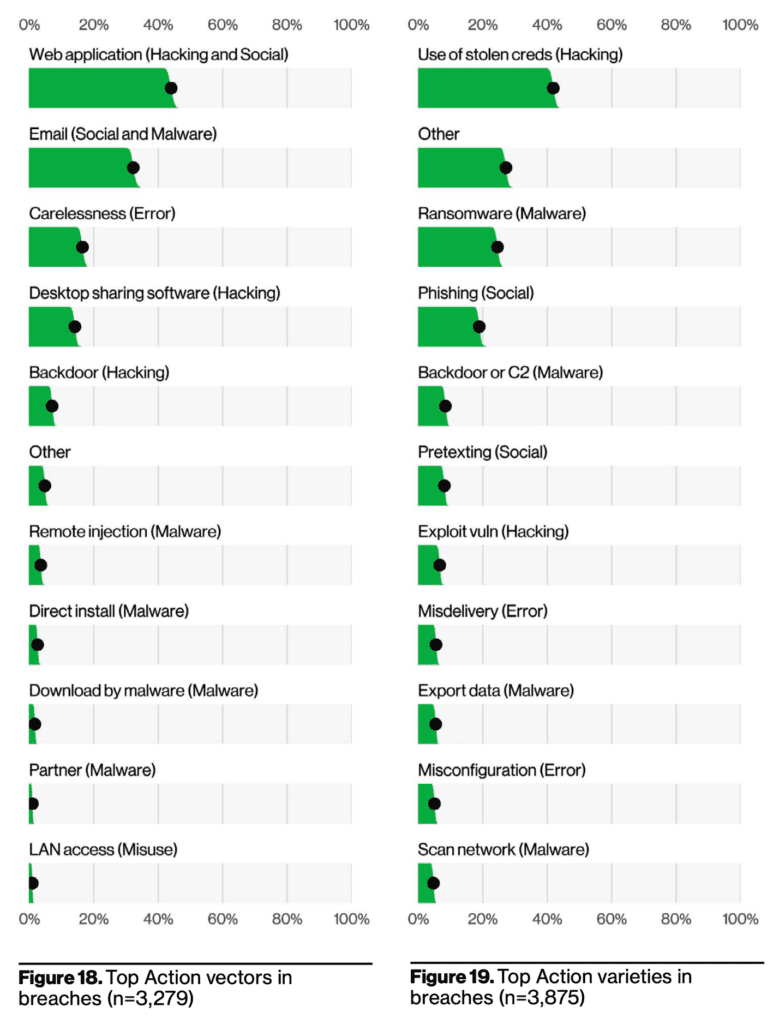
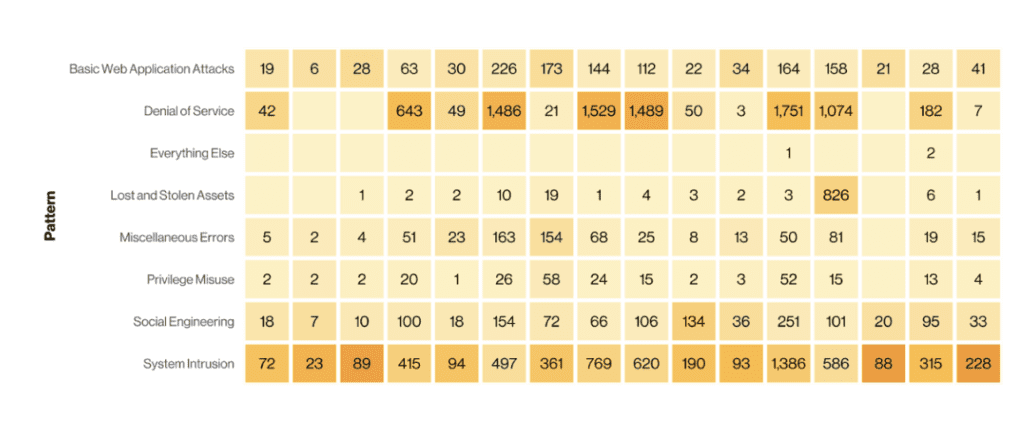
Web application hacking and social engineering, as well as the use of stolen credentials, are all methods used in hacking to gain unauthorized access to computer systems or networks. While they share the common goal of bypassing security measures, there are differences in their techniques and approaches.
As we previously mentioned, web application hacking involves exploiting vulnerabilities in web applications to gain unauthorized access or manipulate their functionality. Attackers may target weaknesses in the application’s code, configuration, or user inputs to carry out various malicious activities. In contrast, social engineering relies on manipulating individuals rather than technical vulnerabilities. Social engineering tactics involve deceiving or tricking people into divulging sensitive information or granting access. It often exploits human psychology, trust, and social dynamics to gain unauthorized entry into systems.
The use of stolen credentials, on the other hand, refers to the act of utilizing login information (such as usernames and passwords) that have been obtained illegally. This can occur through various means, including hacking, phishing, or data breaches. Once the credentials are acquired, hackers use them to gain unauthorized access to systems, networks, or accounts.
While these hacking methods differ in their techniques, they also share some similarities. Firstly, they all involve unauthorized access and the compromise of computer systems or networks. Whether through exploiting vulnerabilities, manipulating individuals, or using stolen credentials, the end goal is to gain unauthorized control or access to sensitive information. Additionally, all three methods require a certain level of technical expertise and knowledge of system vulnerabilities or human behavior.
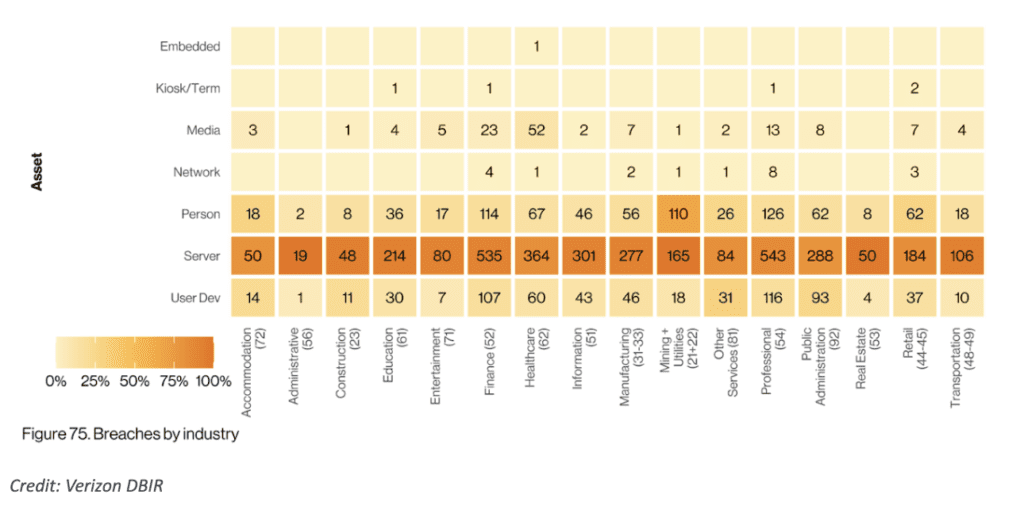
Effect On Our Assets
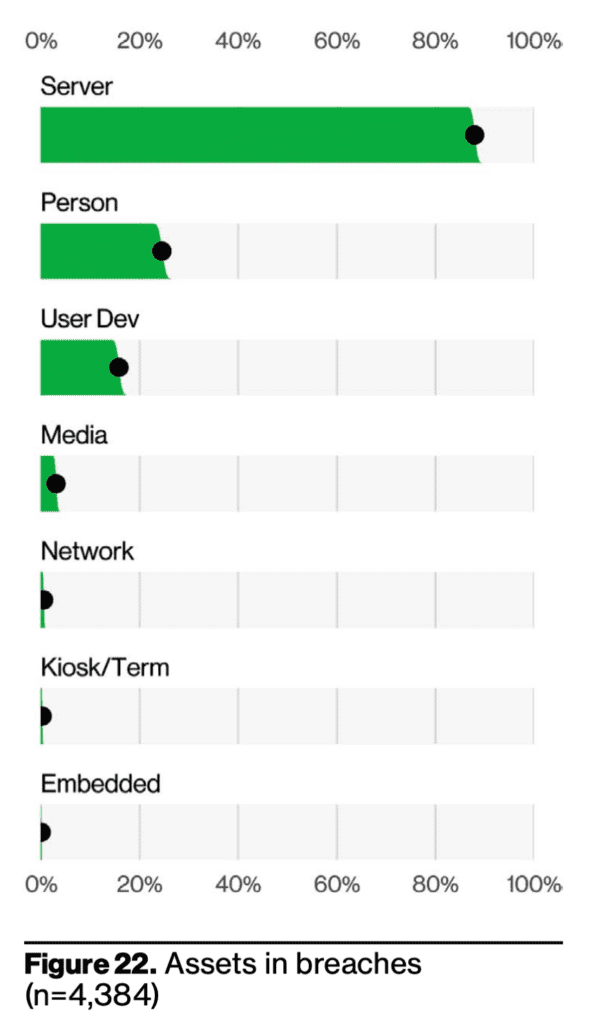
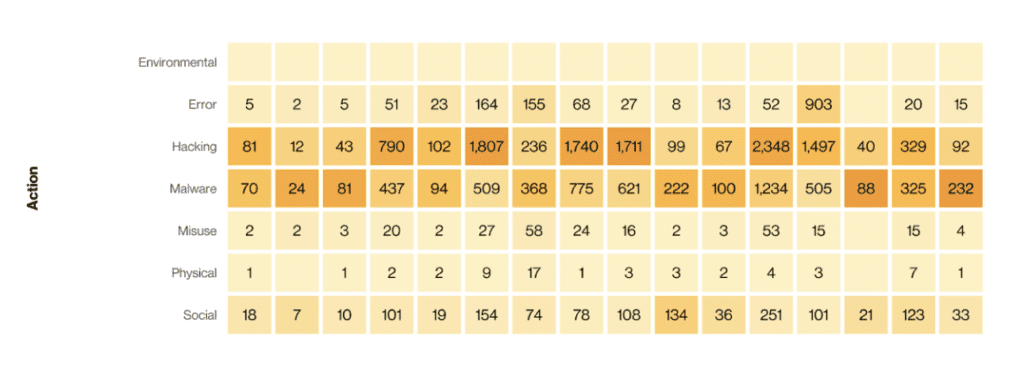
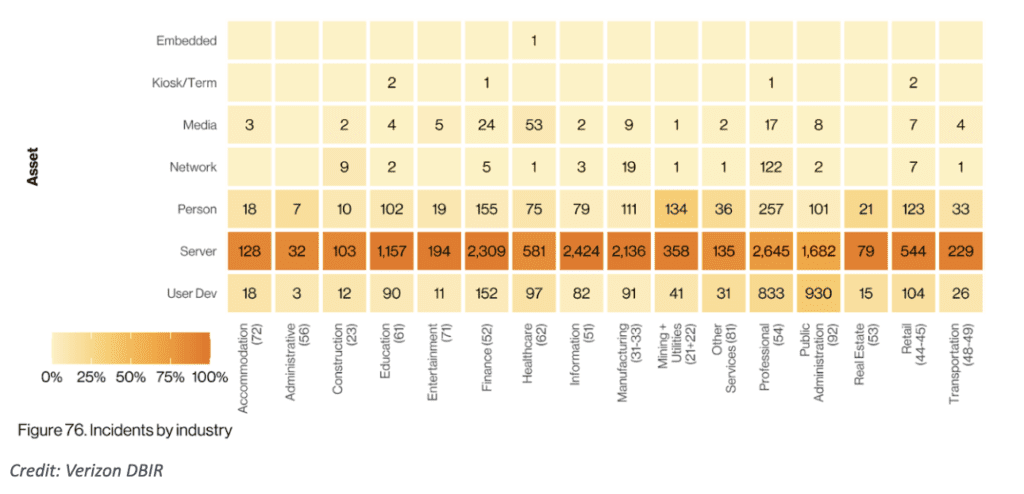
The fact that over 80% of our data is stored in servers and only 20% is stored on people can be intimidating when considering data breaches. While the majority of data stored in servers may be vulnerable to hacking and other cyber threats, the data stored on people is often compromised through social engineering attacks.
When data breaches occur, the vast amount of information stored in servers becomes an attractive target for hackers. These breaches can lead to the exposure of personal data, such as names, addresses, financial details, and even sensitive health records. As our reliance on technology and online services increases, the volume of data stored in servers also grows, making them an appealing target for cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities in these systems.
On the other hand, the data stored on people themselves, such as their behaviors, preferences, and personal interactions, is often targeted through social engineering attacks. Social engineering involves manipulating individuals through deception or psychological tactics to trick them into revealing sensitive information or granting unauthorized access. Attackers may impersonate trustworthy entities, employ phishing techniques, or exploit human psychology to gather valuable data directly from individuals.
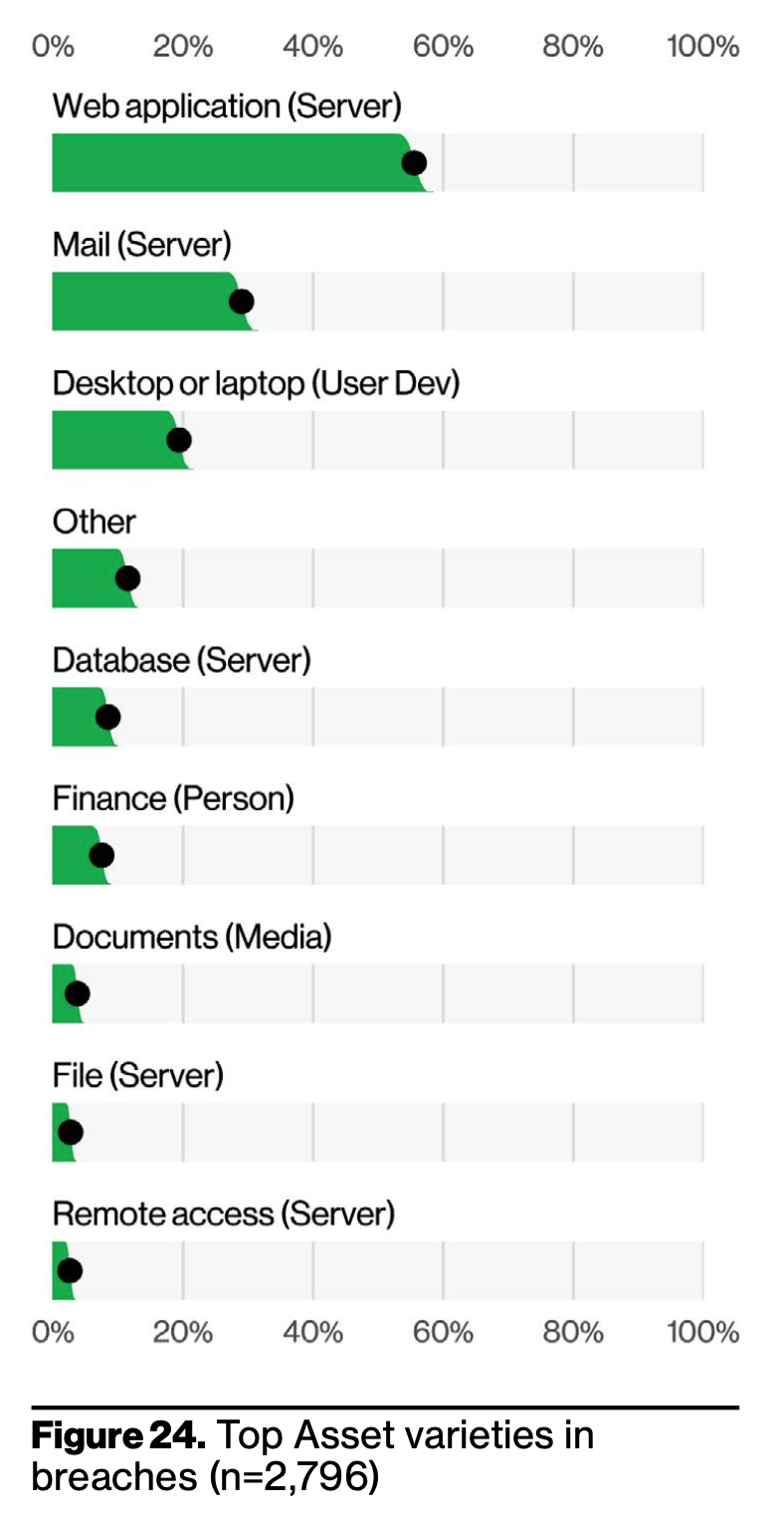
The statistics reveal that almost 60% of compromised assets are located on web application servers, indicating the vulnerability of these systems. Additionally, 25% of compromised assets are found on mail servers, while 20% are on desktop or laptop devices used by individuals.
The high percentage of compromised assets on web application servers is alarming due to the critical role these servers play in storing and processing sensitive data. Web applications are often targeted by hackers seeking to exploit vulnerabilities in the software or gain unauthorized access to databases containing valuable information. Breaches in these servers can result in the exposure of personal and financial data, leading to identity theft, fraud, and other forms of cybercrime.
Similarly, the compromise of assets on mail servers is a cause for concern. Email is a common communication channel used for both personal and business purposes, often containing sensitive information. Attackers may exploit vulnerabilities in mail servers to intercept or manipulate emails, compromising the confidentiality and integrity of communications. Breaches involving mail servers can have severe consequences, including unauthorized access to sensitive data, unauthorized email forwarding, or even email account takeover.
Lastly, the compromise of assets on desktop or laptop devices highlights the risk posed to individual users. These devices often store personal information, credentials, and access to various online accounts. User devices are targeted through malware, phishing attacks, or social engineering, with the goal of stealing sensitive data or gaining unauthorized access to online accounts.
Our Solution
To protect business assets from potential cyber events, integrating uniquely designed insurance coverages like errors and omissions (E&O) coverage and media liability coverage can be beneficial. E&O coverage, also known as professional liability insurance, provides protection against claims arising from professional mistakes, negligence, or failure to perform professional services. Media liability coverage, on the other hand, specifically addresses risks associated with media-related activities such as publishing, advertising, or broadcasting.
By integrating these insurance coverages, businesses can mitigate financial losses resulting from cyber-related incidents. E&O coverage can safeguard against claims arising from errors or omissions in professional services, including those related to cybersecurity. It can help cover legal defense costs, settlements, or judgments in the event of a lawsuit due to alleged professional negligence or failure to provide adequate cybersecurity measures.
Similarly, media liability coverage offers protection against claims related to media content, such as defamation, copyright infringement, or invasion of privacy. In the context of cyber events, this coverage can be valuable for businesses involved in digital media, social media management, or content creation. It can help cover legal expenses and damages resulting from cyber-related issues associated with media content, such as accidental dissemination of sensitive information or intellectual property violations.
By integrating these insurance coverages, businesses can proactively shield themselves from potential financial repercussions caused by cyber events. However, it’s important to carefully
review the policy terms, conditions, and exclusions to ensure the coverage aligns with the specific needs and risks of the business. Consulting with an insurance professional or broker experienced in cyber liability insurance can provide valuable guidance in selecting the appropriate coverage options for comprehensive protection.